Injection molding Processing of Plastic
One of the most common processing methods for plastics is injection moulding. Nowadays wide range of articles are made by means of injection molding. These include such things as electric drill casing, television housings, gearwheels etc.
The original injection moulding machines are based on the pressure die casting techniques for casting metals. The first machine is reported to have been patented in the United States in 1872, specifically for use with celluloid. this was an important invention but probably before its time because in the following years very few developments in injection moulding processes were reported and it was not until the 1920s, in Germany, that a renewed interest was taken in the process. The first German machines were very simple pieces of equipment and relied totally on manual operation.
In the late 1930s the next major development in injection molding , i.e. the introduction of the hydraulically operated machines get available. However, these machines still tended to be hybrids based on the die casting technology and the design of injection moulding machines for plastic was not taken really serious until the 1950s when a new generation of equipment was developed.
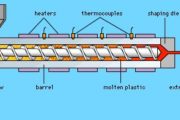
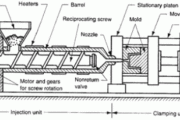
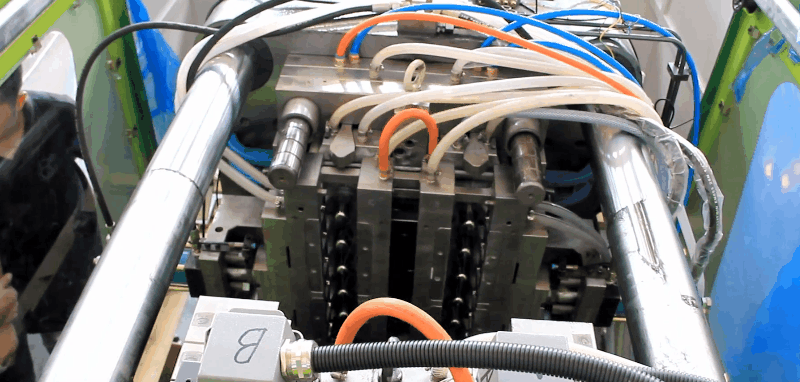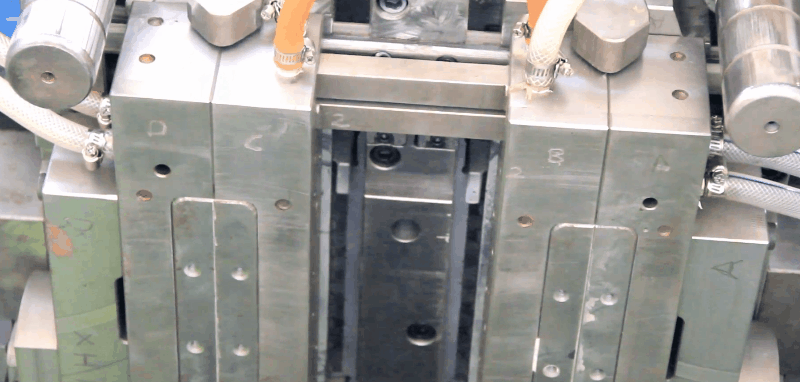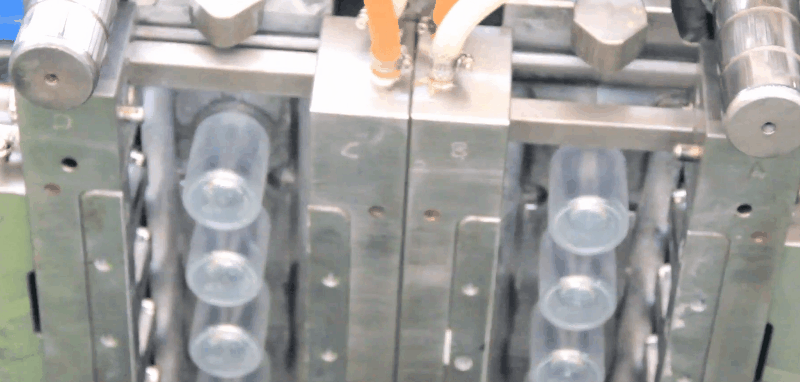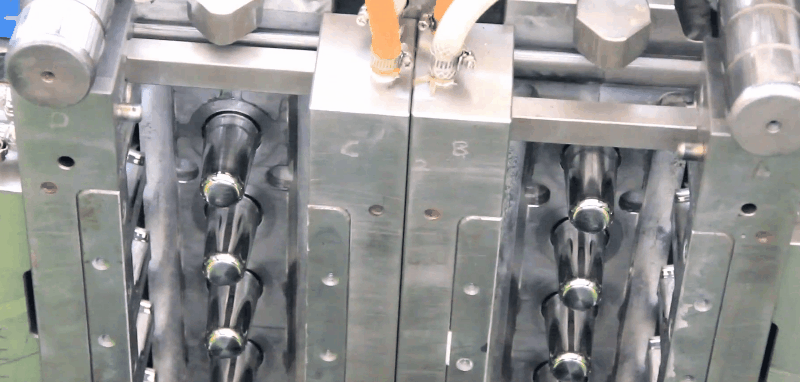
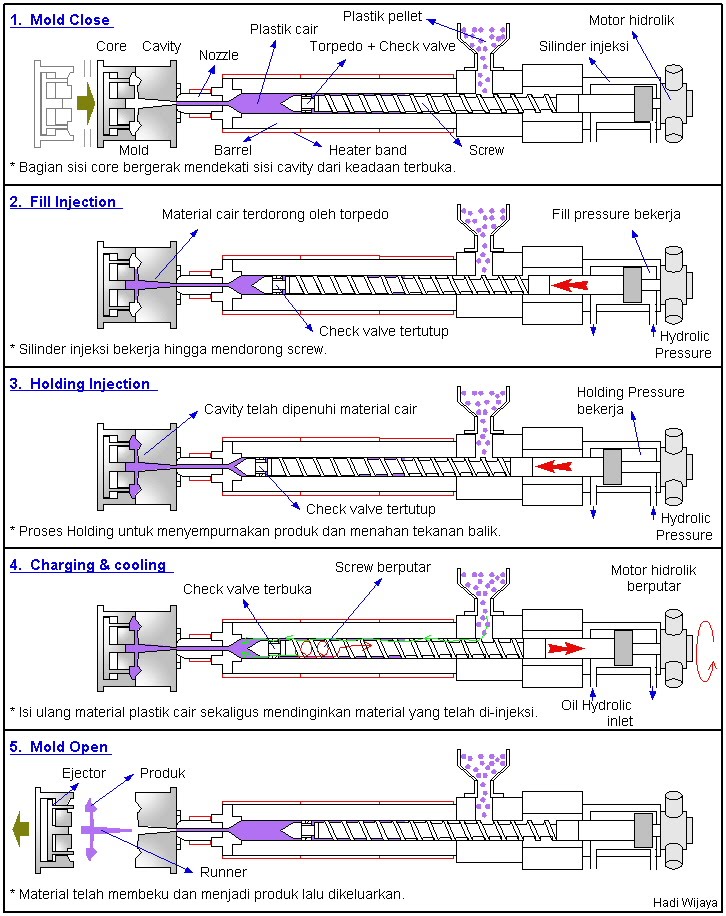
Basically, injection moulding is a simple process. A thermoplastic, in the form of granules or powder, passes from the feed hopper into the barrel where it is heated so that it becomes soft. It is then forced through a nozzle into the relatively cold mould which is clamped tightly closed. When the plastic has had sufficient time to become solid the mould opens, the article is ejected and the cycle is repeated. The major advantages of the process include its versatility in moulding a wide range of products, the ease with which automation can be introduced, the possibility of high production rates and the manufacture of articles with close tolerances. The basic injection molding concept can also be adapted for use with thermosetting materials.