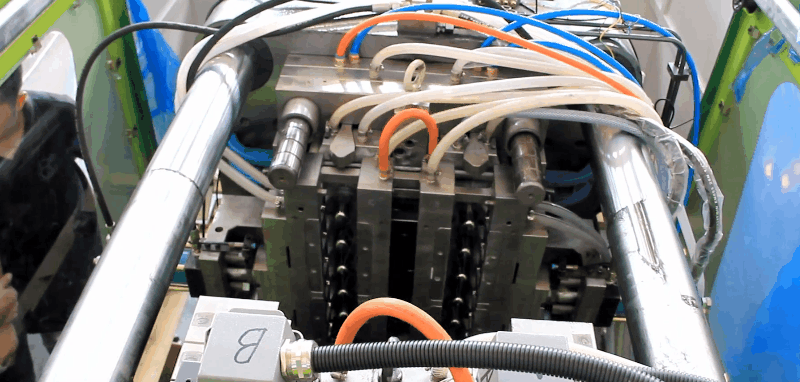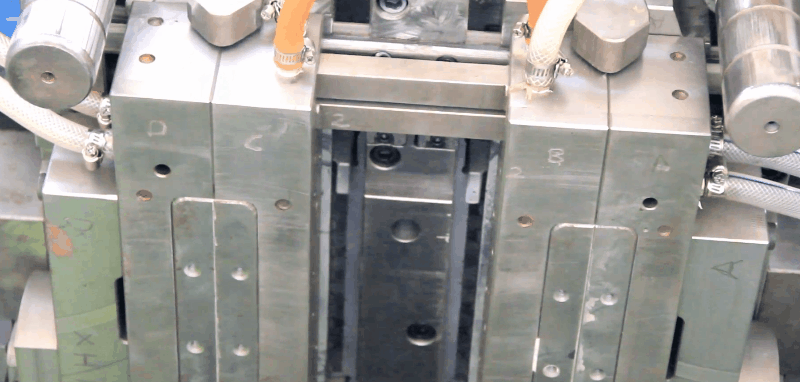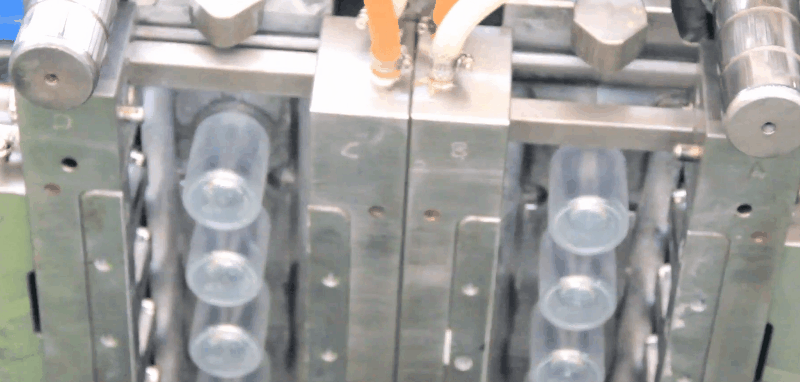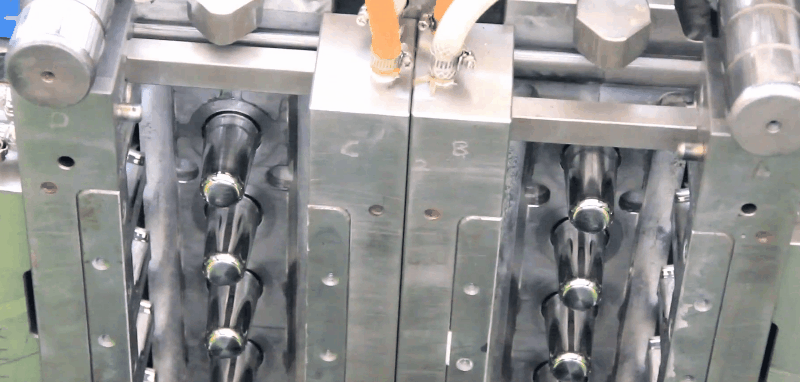
PET Preform Heating Temperature is about 75°C to 130°C on the preforms. So it will need to be adjusted according to the PET preforms` height, thickness, workshop indoor temperature, etc. A reheating step is then necessary to condition the preforms to the appropriate temperature distribution (slightly above the glass transition, which is typically ~75°C). This stage is generally performed using infrared (IR) heaters, taking advantage of the semi-transparent behavior of PET with regard to IR radiation. the objective function is reduced by 60% of its initial value after the first iteration, and by more than 80% at the end of the optimization process. Consequently, the thickness distribution of the formed bottle is 80% more uniformed after optimization. The algorithm converges after five iterations, which involves only 10 objective-function evaluations (that is to say, 10 FE simulations). On average, one cost-function evaluation requires 26 min CPU. Thus, the total CPU time required for the optimization is ~ 3 h 20 min. PET Preform reheat Temperature versus time inside and outside of the PET preforms for the oven configuration from publication. PET
Read more →Reaction Injection Molding Technique Introduction This process involves the high pressure impingement mixing of two or more reactive liquid components and injected into a closed mold at low pressure. With RIM technology, cycle time of 2 minutes and less have been achieved in production for molding large and thick parts. Principal plastic used is thermopolyurethane (PUR). other material s used are thermoplastic nylon; thermoset polyester and epoxy. The advantages of the RIM over injection molding include the molding of the parts larger than 10 pounds, they can be made on the production basis using thinner walls because of the lower processing viscosities, or using very thick walls because curing is uniform throughout the part. There are problems associated with this method, however. The lack of the suitable internal release has made the RIM process labor-intensive, but changes are now occurring to significantly reduce or eliminate this problem. The molded polyurethane faithfully reproduces the surface of the mold and tends to stick to them. Originally the application of the mold-release agents was necessary with each cycle of the RIM technology. After
Read more →Mold Temperature Control in Plastic Injection Molds If we want to get efficient moulding, we should control the mould temperature and this is done by means of passing fluid through a suitable arrangement of channel in the mould. The rate at which the moulding cools affect the total cycle time as well as the surface finish, tolerances, distortion and internal stresses of the moulded article. High mould temperature improves the surface gloss and tend to eliminate voids. If the mould temperature is too low then the material may freeze in the cavity before it is filled.
Read more →Stretch Blow Molding Technique Introduction The stretch-blow process can give many resins improved physical and barrier properties. In biaxial orientation, bottles are stretched lengthwise by an external gripper, or by internal stretch rod, and then stretch radially by blow air to form the finished container against the mold walls. This process aligns the molecules along two planes, providing additional strength and even more important, better barrier properties then are possible without biaxial orientation. Other advantages include better clarity, increase impact strength, or toughness, and reduce creep. The actual increase is dependent on the ratio of blow-up in each direction. Stretch blow molding is possible for thermoplastic materials such as PET, PVC, polystyrene, acrylonitrile, polypropylene, and acetals. The amorphorous material with the wide range of thermoplasticity are easier to Stretch blow than the partially crystalline types. With the partially crystalline type, if the crystallizing is too rapid, the bottle is virtually destroyed. Stretch-blow processing can be separated into two categories: in-line and two-stage. In-line processing is done on a single machine, while two stage processing requires an injection line to produce
Read more →Injection Blow Molding Technique Introduction In injection blow molding, a preform is formed by a conventional injection molding machine plasticator. The injection molding machine injector provides an optimum plastics melt, with the uniformly homogeneous melt that is repeatable. This plastic melt is injected into the preform cavity forming the preform around the core rod. In tool design the core rod and the parison are very important. Each container to be blow molded has its unique parison and core rod design. The second stage consists of transferring the injection molded preform, via either the core rod or the neck ring, into the blow mold. At this station compressed air enters through the core rod or seal ring, and the preform is blown into the blow mold configuration . It is held in the cold blow mold until the material is set, and then the air is exhausted and the blown bottle ejected. Machines are used with from two to six stations. In the two-station machine, the finished container is ejected after the blow mold opens at the blow station by air
Read more →Venting of Plastic Injection Molds Before the plastic melt is injected, the cavity in the closed mould contains air. When the melt enters the injection mould, if the air cannot escape it become compressed. At worst this may effect the filling, but in any case the sudden compression of the air causes heating. This may be sufficient to burn the plastic and the mould surface at the local hot spots. To alleviate this problem, vents are machined into the mating surfaces of the plastic injection mould to allow the air to escape.
Read more →Injection Molds in Injection Molding Machines An injection mold consists of two halves into which the impression of the part to be moulded is cut. The mating surfaces of the mould halves are accurately machined so that no leakage of the plastic can occur at split line. If leakage does occur the flash on the moulding is unsightly and expensive to remove. In order to facilitate mounting the mould in the machine and cooling and ejection of the moulding, several additions are made to the basic mould halves. 1. Backing plates permit the mould to be bolted on to the machine platens. 2. Channels are machined into the mould to allow the mould temperature to be controlled. 3. Ejector pins are included to that the moulded part can be freed from the mould. The mould cavity is joined to the machine nozzle by means of the sprue. The sprue anchor pin then has the pulling the sprue away from the nozzle and ensuring that the moulded part remains on the moving half of the mould, when the mould opens. For
Read more →Extrusion Blow Molding Technique Introduction In extrusion blow molding, a parison is formed by an extruder. The plastic pellets are melted by heat which is transferred from the barrel and by the shearing action of the extruder screw as they pass through the extruder. The helical flights of the screw change configuration along its length from input to output ends to ensure a uniformly homogeneous melt. Turning continuously the screw feeds the melt through the die head as an endless parison or into an accumulator. The size of the part and the amount of the material necessary to produce the part (shot size) dictate whether or not an accumulator is required. The non-accumulator machine offers an uninterrupted flow of the plastic melt. With the accumulator the flow of the parison through the die is cyclic. The connecting channel between the extruder and the accumulator, and within the accumulator itself, are design rheologically to prevent restrictions that might impede the flow or cause the melt to hang up. Flow part should have low resistance to melt flow to avoid placing an
Read more →Blow Molding Techniques Introduction Hollow plastics products such as a squeeze bottles, milk bottles, fuel tanks, toys, oil containers, chemical tanks, furniture, electrical housing, are blow moulded. Different processes are used but basically all of them are similar. The basic process involves producing a plastic parison or preform (tube, pipe, or test tube plastic shape), placing this preform into a closed two plate mold, injection of air into the heated parison to blow it out against the mold cavity, cooling of the expanded parison, opening of the mold, and removing the rigid blow molded part. Blow molding technique basically divided into three categories, namely, the extrusion blow molding process which principally uses as unsupported parison, and the injection blow molding process which uses a preform supported on a metal core pin. The third major category is called the stretch-blow molding process. Stretch-blow molding can be started with either the extrusion or injection blow molding process. By stretching at prescribed temperature the properties of many plastics can be significantly improved providing cost / performance advantages. These processes provide different advantages to
Read more →Electrical Control system on Injection Moulding Machines – By Zafar Kamal The electrical control system serves as the nerve and memory center to program and sequence the machine cycles. Its purpose is to sense, program the results, and cause an action to take place. Position is sensed through the use of the limit switches, change in the heat through thermocouples, and changes in pressure through pressure switches. After analyzing the incoming signals and making a programmed decision, the control system passes this decision on to the pilot operating devices which convert the electrical signal into mechanical motions, thus resulting in the desired action. There are specific type of the devices available for the different functions. First, There is motor or prime mover , and then the sensing devices, next, control systems such as motor starters, heater contractors and relays, and finally , the ultimate load controls such as solenoids or heater bands. The electric motor or motors used in the average injection press must have a high breakdown torque. Most motors operate on 220 or 440
Read more →Electrical System introduction of Injection Molding Machines – By Zafar Kamal For better and accurate functions, the injection-molding machine follows a programmed sequence of events for the precise control of heat, the proper timing of injection pressures and cooling, and special machine sequences, and the ever-dominant need for safety of personnel and equipment. Most injection that the operator has the fundamental knowledge of the machine’s electrical circuits.
Read more →Hydraulic Fluids and Hydraulic Accessories in Injection Molding Machines – By Zafar Kamal 4.3 Hydraulic Fluids If the heating cylinder of the molding machine can be treated as the heart of the system , then it follows the hydraulic-oil lines are the blood of the process. The selection of the oil is very important factor , therefore serious consideration should be taken while selecting the oil. Please contact your machine`s manufacturer for what exactly kind of hydraulic-oil their machines is best selection. 4.4 Hydraulic Accessories All modern molding-machine are equipped with the necessary filtering systems, and a part of any good maintenance program includes the regular inspection of these systems. Maintaining the hydraulic fluid at the proper tank level, making sure that the injection machine is operated at the proper temperature levels, and assuring that the oil is being cleaned and filtered are all-important to the continued trouble-free operation of the machine. The other type of the system which is very important in case of accuracy acheivement is called an electrical system.
Read more →