Injection Blow Molding Technique Introduction
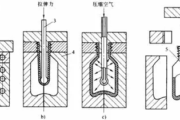
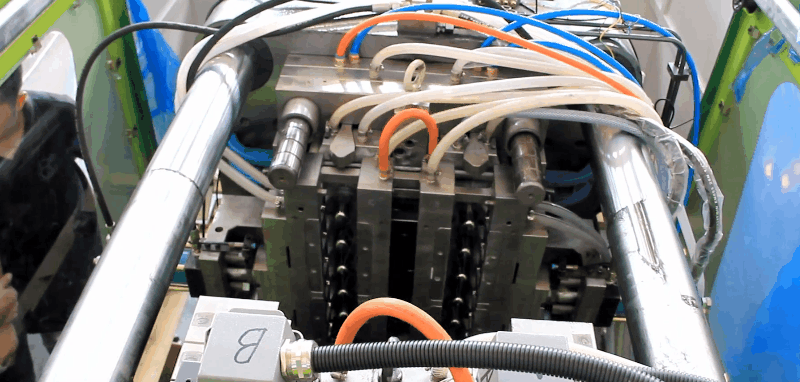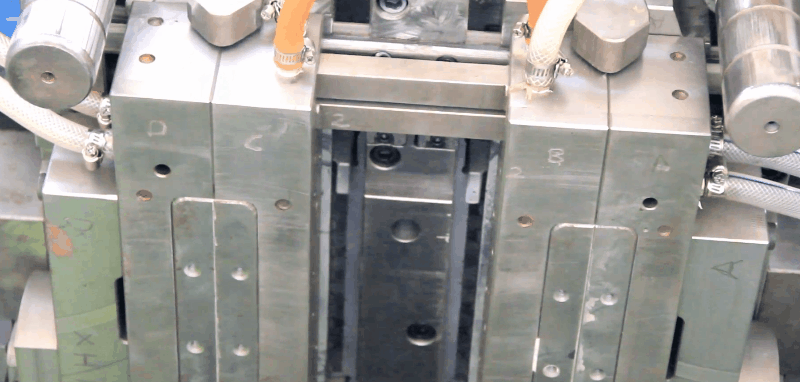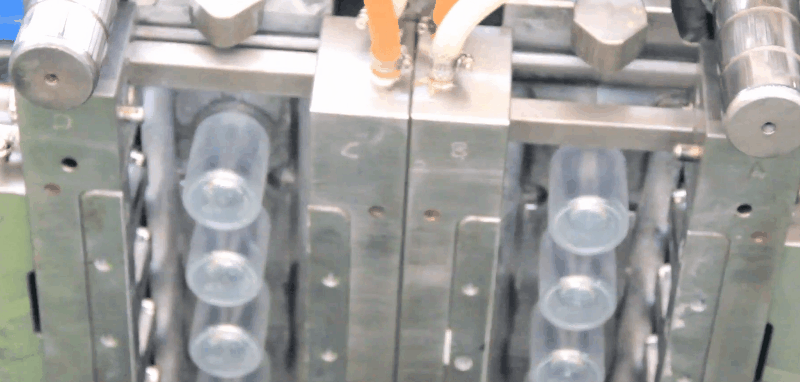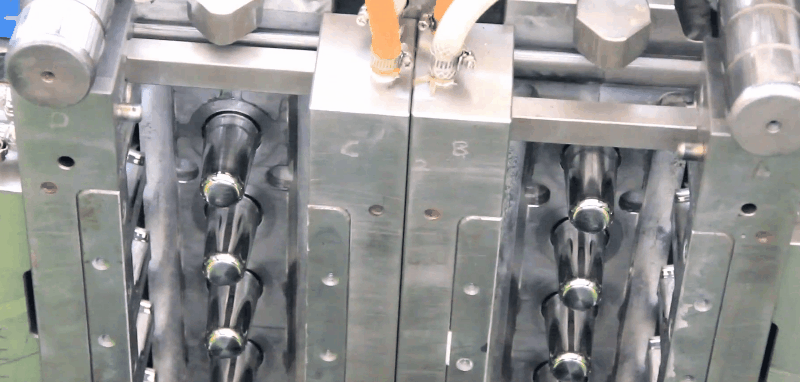
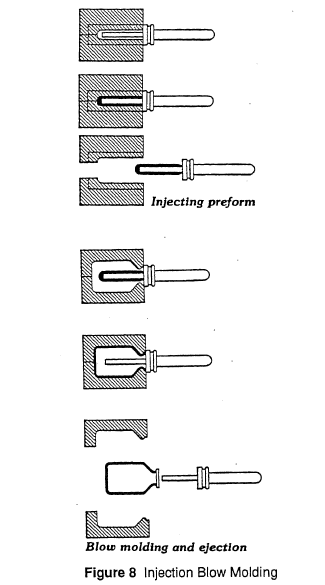
In injection blow molding, a preform is formed by a conventional injection molding machine plasticator. The injection molding machine injector provides an optimum plastics melt, with the uniformly homogeneous melt that is repeatable. This plastic melt is injected into the preform cavity forming the preform around the core rod.
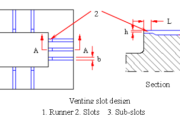
In tool design the core rod and the parison are very important. Each container to be blow molded has its unique parison and core rod design.
The second stage consists of transferring the injection molded preform, via either the core rod or the neck ring, into the blow mold. At this station compressed air enters through the core rod or seal ring, and the preform is blown into the blow mold configuration . It is held in the cold blow mold until the material is set, and then the air is exhausted and the blown bottle ejected.
Machines are used with from two to six stations. In the two-station machine, the finished container is ejected after the blow mold opens at the blow station by air pressure or by mechanical means. In the more conventional threestation machine, the finished container stays with the core pin as it is indexed to the third station where ejection take place. Four, five and six-station machines are available. These additional stations are used for further processing of the containers, such as decorating, position of the blown parts, filling. There have been several type of machines available with different methods of transporting the core rod from one station to other. These include the shuttle, two-position rotary, axial movement, and rotary with three or more stations used in the conventional injection molding clamping units.
– By Zafar Kamal