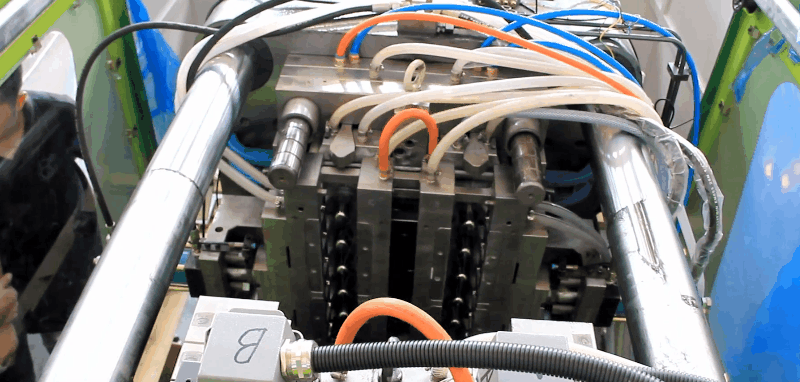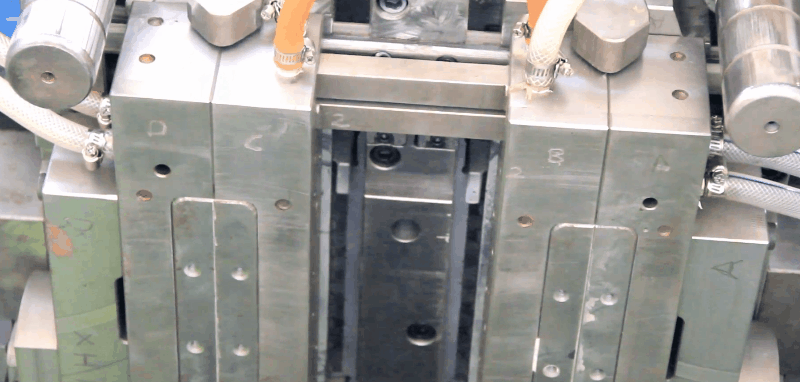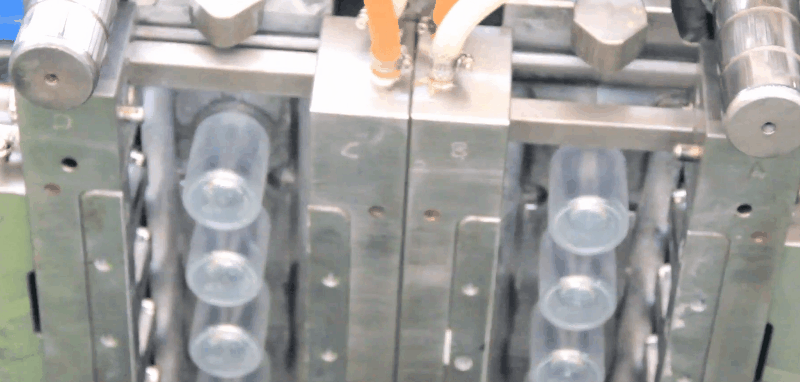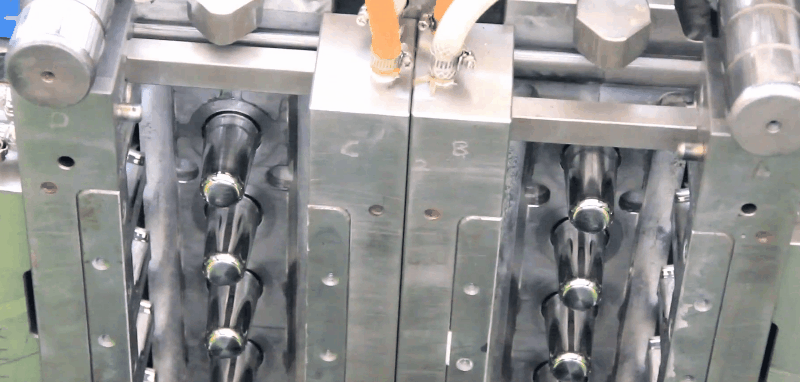
Polystyrene (PS) is an inexpensive and hard polymer that is used extensively.
Typical Applications of Polystyrene (PS)
Packaging
Housewares
– tableware
– trays
Electrical
– transparent housings
– light diffusers
– insulating film
Plastic PS Injection Molding Processing Conditions
| Conditions Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Drying | Not usually required unless stored improperly. If drying is needed, the recommended conditions are 2-3 hours at 80°C [176°F]. |
| Melt Temperature | 180°C–280°C [356°F–536°F]; upper limit is 250°C for flame retardant grades [19–158°F] |
| Mold Temperature | Suggested: 20°C–70°C [68°F–158°F] |
| Material Injection Pressure | 20–60 MPa |
| Injection Speed | Fast speeds are recommended. |
Runners and Gates of PS Injection Mold
All types of conventional gates can be used.
Chemical and Physical Properties of Polystyrene (PS)
General-purpose PS is produced by the polymerization of styrene. Most commercial grades are clear, amorphous polymers. PS offers excellent dimensional and thermal stability, optical clarity, and very little tendency to absorb moisture. It has good dielectric properties. It is resistant to water and dilute inorganic acids, but is attacked by strong oxidizing acids such as concentrated sulfuric acid, and is swollen by some organic solvents.
Processing shrinkage is typically between 0.4–0.7%.