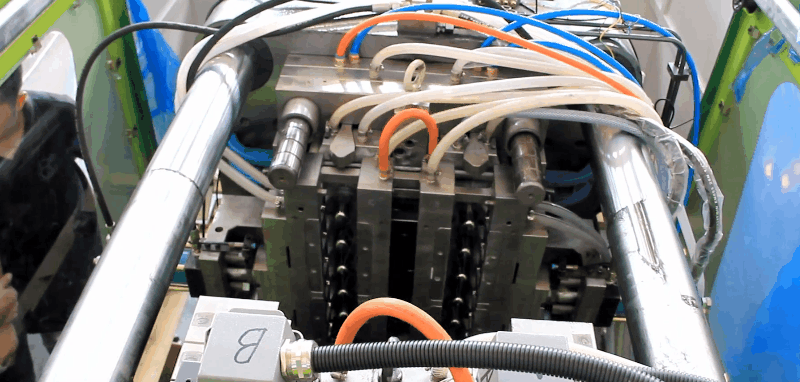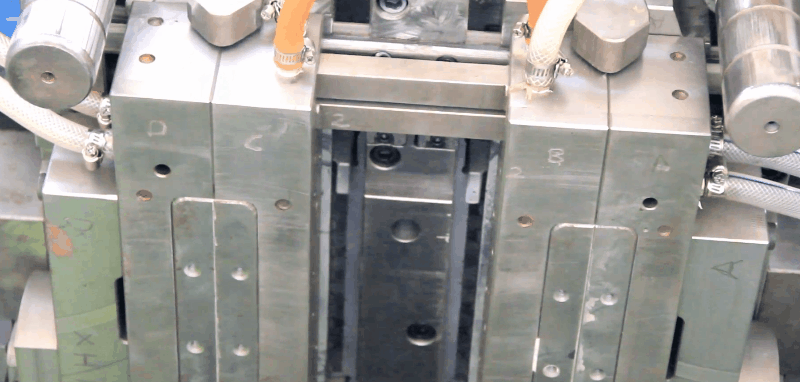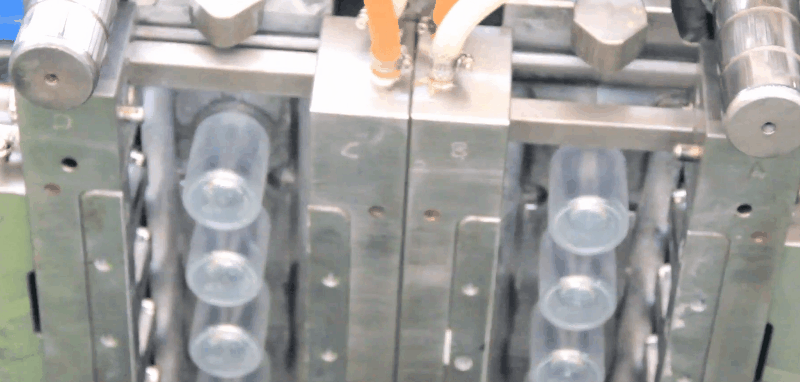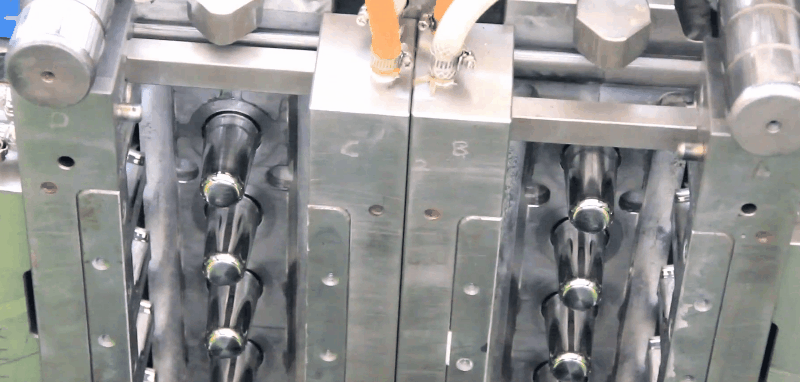
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) has excellent chemical and weather resistance.
Typical Applications of Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
Automotive
– signal light devices
– instrument panels
Blood cuvettes
Industrial
– video discs
– lighting diffusers
– display shelving
Consumer
– drinking tumblers
– stationery accessories
Plastic PMMA Injection Molding Processing Conditions
| Conditions Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Drying | PMMA is hygroscopic and must be dried prior to molding. Drying at 90°C [194°F] for 2-4 hours is recommended. |
| Melt Temperature | 240°C–280°C [460°F–536°F] |
| Mold Temperature | 35°C–80°C [90°F–176°F] |
| Injection Speed | Moderate |
Chemical and Physical Properties of Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
Pellets for injection molding are made by bulk polymerization of methyl methacrylate followed by extrusion and pelletization, or by polymerization in an extruder. Formulations vary by molecular weight and physical properties such as flow rate, heat resistance, and toughness. Higher molecular weight grades are tougher than lower molecular weight grades. High flow formulations are generally preferred for molding.
Heat deflection temperature under load varies from 75°C [167°F] for high flow materials to 100°C [212°F] for low flow (high molecular weight) materials.
PMMA has excellent optical properties and weatherability. The white light transmittance is as high as 92%. Molded parts can have very low birefringence, which makes PMMA suitable as a material for video discs.
PMMA exhibits room temperature creep. The initial tensile strength is high but under long-term, high-stress loading, it exhibits stress craze. Impact strength is good but it does show some notch sensitivity.