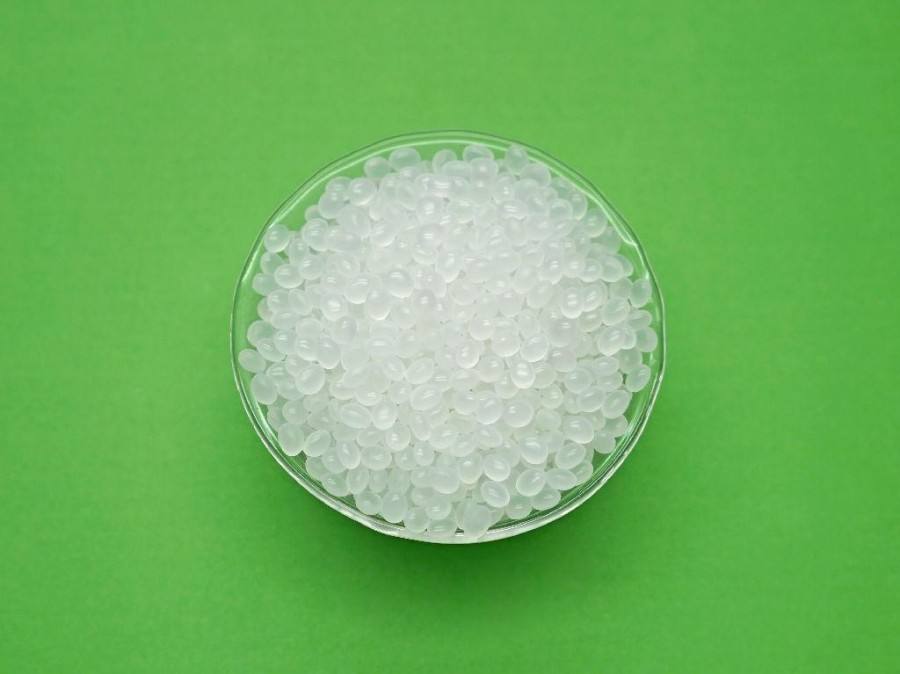
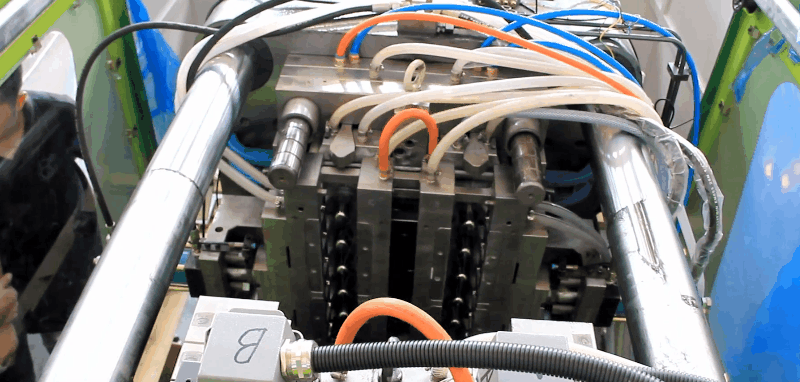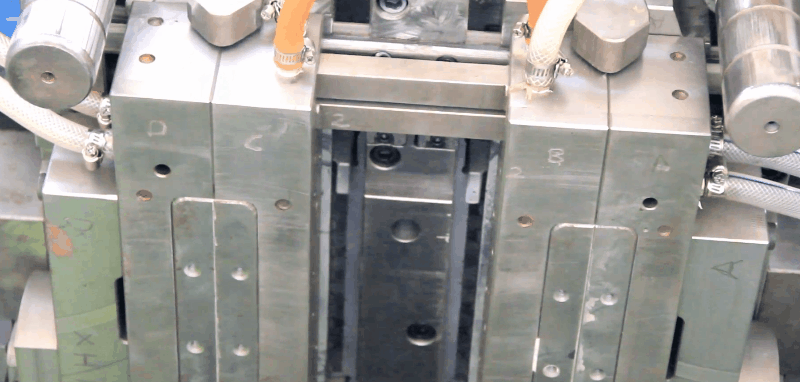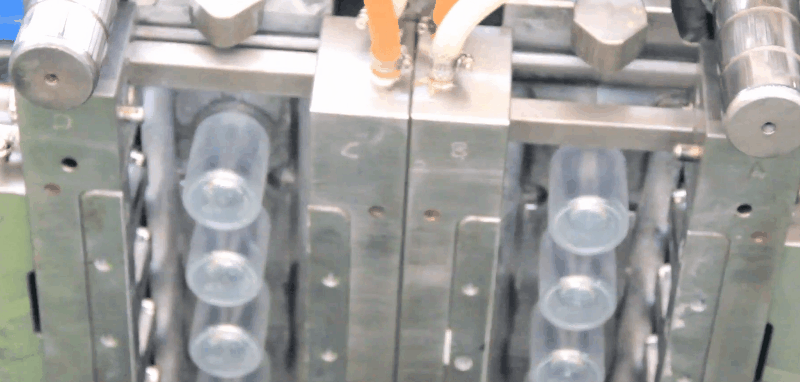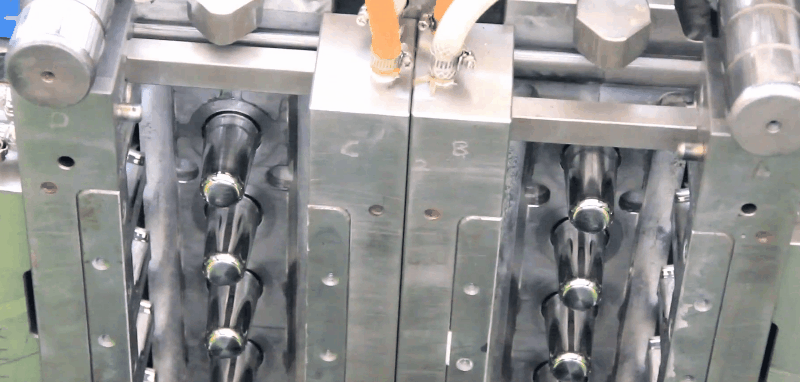
Glycol-modified PET and copolyesters (PETG) offer a desirable combination of properties such as clarity, toughness, and stiffness.
Typical Applications of Glycol-modified PET and copolyesters (PETG)
– medical devices
– test tubes
bottles
toys
displays and lighting fixtures
face shields
refrigerator crisper pans
Plastic PETG Injection Molding Processing Conditions
| Conditions Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Drying | Drying is essential for PETG prior to injection molding. The moisture level must be below 0.04%. Drying temperature is not to exceed 66°C [150°F]. Drying at approximately 65°C [149°F] for 4 hours is recommended. |
| Melt Temperature | 220°C–290°C [428°F–554°F]; the melt temperature is grade specific |
| Mold Temperature | 10°C–30°C [50°F–86°F], recommended 15°C [60°F] |
| Material Injection Pressure | 30 MPa-130 MPa |
| Injection Speed | High speeds without causing embrittlement |
Chemical and Physical Properties Glycol-modified PET and copolyesters (PETG)
PETGs (or copolyesters) are glycol-modified PETs. The modification is achieved by adding a second glycol during polymerization. The resulting molecular structure is irregular and the material is clear and amorphous with a glass transition temperature of 88°C [190°F]. PETGs can be processed over a wider processing range than conventional PETs and offer a good combination of properties such as toughness, clarity, and stiffness.