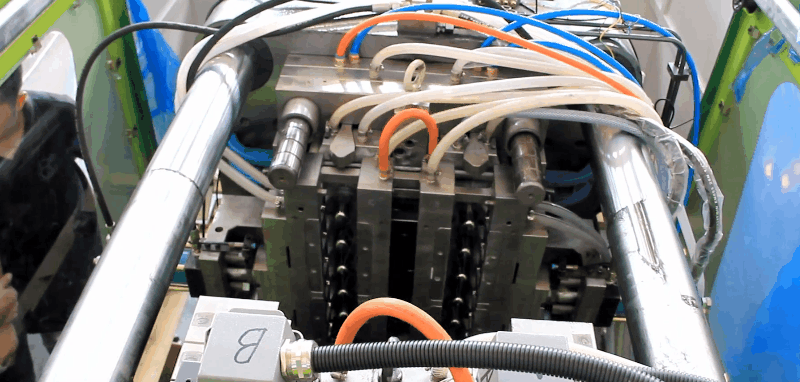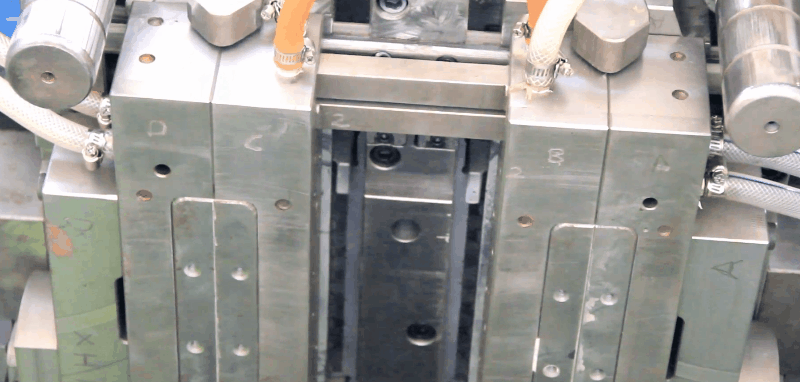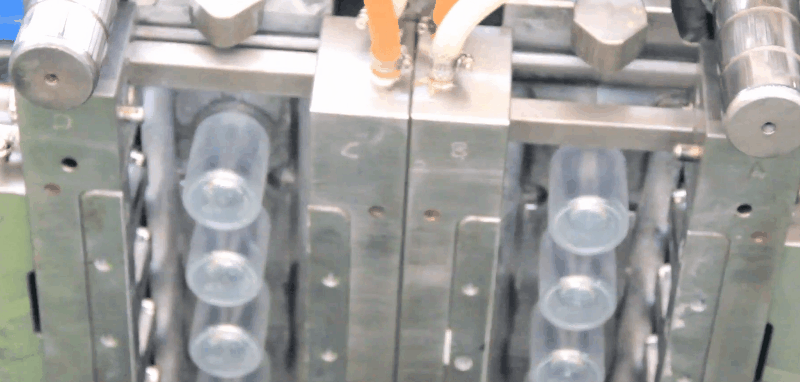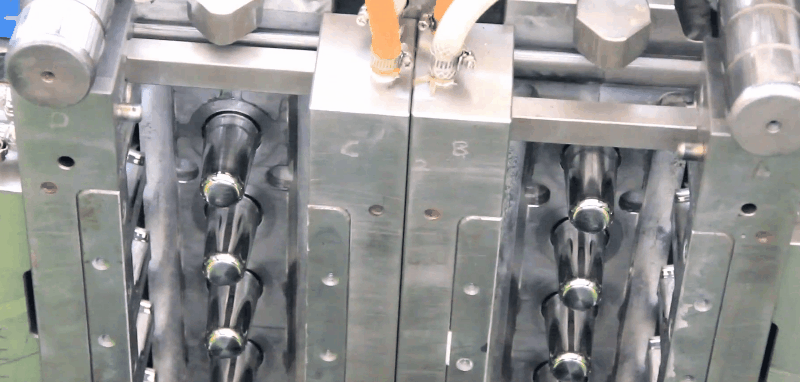
LDPE (Low Density Polyethylene) is an odourless, tasteless and nontoxic polymer that is suitable for food contact applications. LDPE has higher impact strength than HDPE, but lower tensile strength, viscosity, and chemical resistance.
Typical Applications
closures
bowls
bins
pipe couplings
Plastic LDPE injection molding processing conditions
| Conditions Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Drying | Not usually necessary |
| Melt Temperature | 180°C–280°C [355°F–535°F] |
| Mold Temperature | 20°C–70°C [68°F–158°F] |
| Material Injection Pressure | Up to 150 MPa |
| Pack Pressure | Up to 75 MPa |
| Injection Speed | Fast speeds are recommended; profiled speeds can limit warpage problems of large surface area parts. |
Runners and Gates of Injection Moulding Molds
All conventional types can be used; LDPE is suitable for hot runner molds. Insulated hot tip runners are preferred for frequent color changes.
Chemical and Physical Properties of LDPE
LDPE is produced by the polymerization of ethylene at high pressure and temperature. The material is semicrystalline-crystalline. The crystallinity level is low because of chain branching. The material is tough but possesses moderate tensile properties and exhibits creep. However, it has good impact and chemical resistance. It is an easy flow material because of long chain branching.
Commercial materials have densities in the range of 0.91–0.94 g/cm⊃3;. LDPE is permeable to gases and vapors. Very close tolerances are not possible with this material and its relatively large coefficient of thermal expansion makes it less suitable for long-term applications.
Shrinkage is of the order of 0.02–0.05 mm/mm [2–5%] when density is between 0.91–0.925 g/cm⊃3;. When density is between 0.926–0.04 g/cm⊃3;, the shrinkage is of the order of 1.5–4%. Actual shrinkage values are dependent on the molding conditions.
LDPE is resistant to many solvents at room temperatures, but aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons cause swelling. Like HDPE, it is also susceptible to environmental stress cracking.