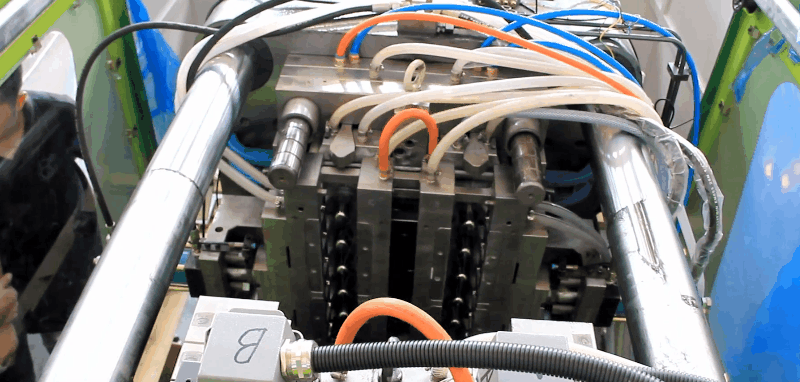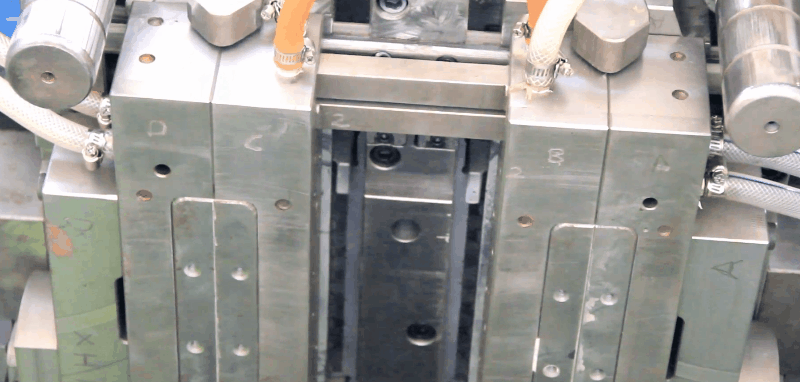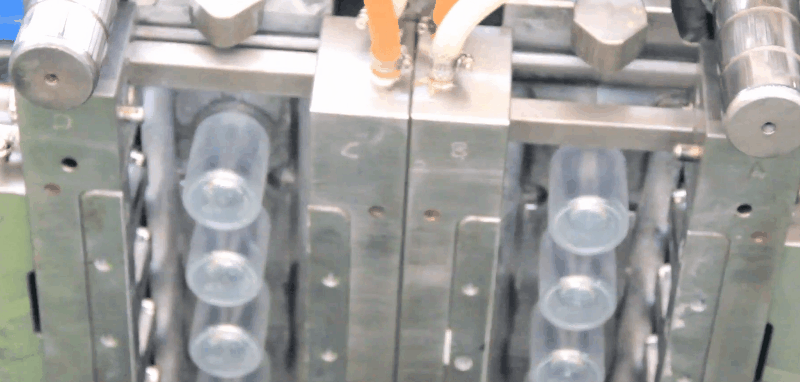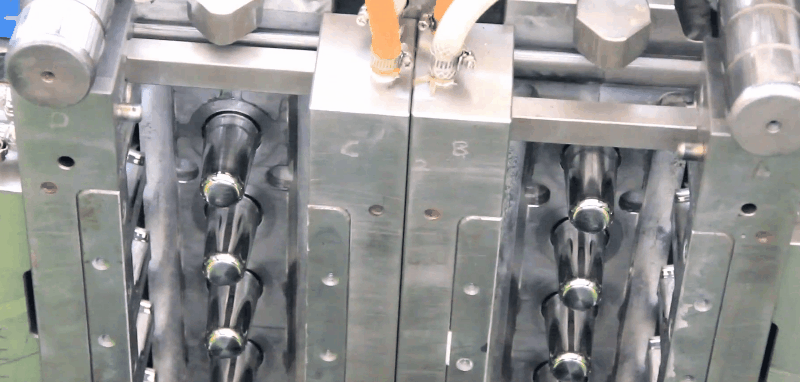
Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) has good rigidity, strength, and toughness, and better chemical resistance than polystyrene. Typical Applications of Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) Electrical – receptacles – mixer bowls – housings – refrigerator fittings – chassis for television sets – cassette boxes Automotive – head lamp bodies – reflectors – glove compartments – instrument panel covers Household applications – tableware – cutlery – beakers Plastic SAN Injection Molding Processing Conditions Gates of SAN Injection Mold All conventional gate types may be used. Chemical and Physical Properties of Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) SAN copolymers are produced by the polymerization reaction of styrene and acrylonitrile. They are strong, transparent materials. The styrene component imparts clarity, stiffness, and processibility and the acrylonitrile component imparts chemical and thermal resistance. They have excellent load bearing capacity, rigidity, good resistance to chemicals, heat deformation, and cyclic temperature loads, and dimensional stability. The properties are dependent on the acrylonitrile content and commercial grades offer different acrylonitrile molecular masses. The addition of glass fibers enhances rigidity and resistance to heat deformation, and decreases the coefficient of linear thermal expansion. The Vicat
Read more →Polystyrene (PS) is an inexpensive and hard polymer that is used extensively. Typical Applications of Polystyrene (PS) Packaging Housewares – tableware – trays Electrical – transparent housings – light diffusers – insulating film Plastic PS Injection Molding Processing Conditions Runners and Gates of PS Injection Mold All types of conventional gates can be used. Chemical and Physical Properties of Polystyrene (PS) General-purpose PS is produced by the polymerization of styrene. Most commercial grades are clear, amorphous polymers. PS offers excellent dimensional and thermal stability, optical clarity, and very little tendency to absorb moisture. It has good dielectric properties. It is resistant to water and dilute inorganic acids, but is attacked by strong oxidizing acids such as concentrated sulfuric acid, and is swollen by some organic solvents. Processing shrinkage is typically between 0.4–0.7%.
Read more →Polyphenylene ether blends (PPE or PPO) are engineering thermoplastics that exhibit resistance to high temperatures. Because of the high glass transition temperature, which is about 210°C, PPEs are often blended with other polymers to increase processability. Typical Applications of Polyphenylene ether blends (PPE or PPO) household appliances – dishwasher – washing machine electrical applications – control housings – fiber-optic connectors Plastic PPE Injection Molding Processing Conditions Runners and Gates of PPE Injection Mold All gates can be used; tab and fan gates are preferred Chemical and Physical Properties of Polyphenylene ether blends (PPE or PPO) PPO is poly(2,6 dimethyl p-phenylene) oxide. The ether linkages offer easier processibility. Copolymers are referred to as PPEs (Polyphenylene Ethers). Typically, the commercially available PPOs (or PPEs) are blended with other thermoplastic materials such as PS (or HIPS), Nylon, etc. These blends are still referred to as PPOs or PPEs. The blends offer superior processibility compared to pure PPOs. Their viscosities are lower. A range of properties can be obtained depending on the ratios of PPO and PS. Blends with nylons (PA 6/6) offer improved
Read more →Polypropylene (PP) is a widely-used, translucent, semicrystalline, thermoplastic polymer with excellent chemical resistance to a range of chemicals. Typical Applications of Polypropylene (PP) Automotive (mineral-filled PP is often used) – dashboard components – ductwork – fans – some under-hood components Appliances – dishwasher door liners – dryer ductwork – wash racks – clothes washer lids – refrigerator liners Consumer products – lawn/garden furniture – lawn mower components – sprinklers Plastic PP Injection Molding Processing Conditions Runners and Gates of PP Injection Mold In the case of cold runners, typical diameters range from 4–7 mm. Full round sprues and runners are recommended. All types of gates can be used. Typical pin gate diameters range from 1–1.5 mm, but diameters as low as 0.7 mm can be used. In the case of edge gating, the minimum gate depth should be half the wall thickness and the width should be at least double the thickness. Hot runners can readily be used for molding PP. Chemical and Physical Properties of Polypropylene (PP) PP is produced by the polymerization of propylene using stereospecific catalysts. Isotactic
Read more →Polyacetal or polyoxymethylene (POM) has a low coefficient of friction, good dimensional stability, and high-temperature resistance. Applications of polyoxymethylene (POM) gears bearings valve and pump housings lawn equipment Plastic POM Injection Molding Processing Conditions Runners and Gates of polyoxymethylene (POM) Any type of gate can be used. Circular tapered gates should be as short as possible. Insulated, hot tip runners are preferred for homopolymers. Both internally and externally heated hot runners can be used with copolymers. Chemical and Physical Properties of polyoxymethylene (POM) Acetals are tough, resilient materials that exhibit good creep resistance, dimensional stability, and impact resistance even at low temperatures. Acetal grades are either homopolymers or copolymers. Homopolymers have better tensile strength, fatigue resistance and hardness, but are difficult to process. Copolymers have better thermal stability, chemical resistance, and processibility. Both homopolymers and copolymers are crystalline and have low moisture absorption. Copolymers can be used continuously at air temperatures up to 100°C [212°F]. Homopolymers have slightly higher temperature resistance. The many grades of acetal materials that are available can be tailored for different applications. High crystallinity levels of
Read more →Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) has excellent chemical and weather resistance. Typical Applications of Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) Automotive – signal light devices – instrument panels Blood cuvettes Industrial – video discs – lighting diffusers – display shelving Consumer – drinking tumblers – stationery accessories Plastic PMMA Injection Molding Processing Conditions Chemical and Physical Properties of Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) Pellets for injection molding are made by bulk polymerization of methyl methacrylate followed by extrusion and pelletization, or by polymerization in an extruder. Formulations vary by molecular weight and physical properties such as flow rate, heat resistance, and toughness. Higher molecular weight grades are tougher than lower molecular weight grades. High flow formulations are generally preferred for molding. Heat deflection temperature under load varies from 75°C [167°F] for high flow materials to 100°C [212°F] for low flow (high molecular weight) materials. PMMA has excellent optical properties and weatherability. The white light transmittance is as high as 92%. Molded parts can have very low birefringence, which makes PMMA suitable as a material for video discs. PMMA exhibits room temperature creep. The initial tensile strength is
Read more →Glycol-modified PET and copolyesters (PETG) offer a desirable combination of properties such as clarity, toughness, and stiffness. Typical Applications of Glycol-modified PET and copolyesters (PETG) – medical devices – test tubes bottles toys displays and lighting fixtures face shields refrigerator crisper pans Plastic PETG Injection Molding Processing Conditions Chemical and Physical Properties Glycol-modified PET and copolyesters (PETG) PETGs (or copolyesters) are glycol-modified PETs. The modification is achieved by adding a second glycol during polymerization. The resulting molecular structure is irregular and the material is clear and amorphous with a glass transition temperature of 88°C [190°F]. PETGs can be processed over a wider processing range than conventional PETs and offer a good combination of properties such as toughness, clarity, and stiffness. Feel Free to Contact Us if Any Questions
Read more →Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) has excellent chemical resistance and barrier properties, good strength, rigidity, fatigue endurance, and abrasion resistance. Typical Applications of Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) Automotive – mirror backs – grille supports – head lamp reflectors – alternator housings Electrical applications – motor housings – electrical connectors – relays – switches – microwave oven interiors Industrial applications – furniture chair arms – pump housings – hand tools – PET bottles and containers Plastic PET Injection Molding Processing Conditions Runners and Gates of PET Injection Mold All conventional types of gates can be used. Gates should be 50–100% of the part thickness. Chemical and Physical Properties PET is an aromatic polyester produced from the polymerization of either terephthalic acid (TPA) or dimethyl ester terephthalic acid (DMT) and ethylene glycol (EG). The glass transition is approximately 165°C [330°F] and the material crystallizes over a temperature range from 120°C–220°C [248°F–428°F]. PET is highly sensitive to moisture at high temperatures and exhibits excessive warpage when reinforced with glass fibers. The promotion of crystallinity is achieved through adding nucleating agents and crystal growth accelerators. Crystalline moldings
Read more →Polyetherimide (PEI) is an amorphous thermoplastic with high-temperature resistance, strength, and stiffness. Typical Applications of Polyetherimide (PEI) Automotive – engine components – temperature sensors – fuel and air handling devices Electrical/electronics – connector materials – printed circuit boards – circuit chip carriers – explosion-proof boxes Packaging applications Interior aircraft materials Medical – surgical staplers – tool housings – non-implant devices Plastic PEI Injection Molding Processing Conditions Chemical and Physical Properties of Polyetherimide (PEI) The chemical structure of PEI consists of repeating aromatic imide and ether units, which accounts for its high temperature resistance. This structure also leads to high stiffness and modifiers are used to make the material processible. PEIs are very stiff and strong even without reinforcements, and they have excellent thermal stability so they can be used in high temperature applications. They also have good flame and chemical resistance, and effective electrical insulation properties. The glass transition temperature is high (215°C [419°F]). PEI exhibits low shrinkage and highly isotropic mechanical properties.
Read more →Polycarbonate and polybutylene terephthalate blends (PC+PBT) combine the properties of PC and PBT, including the high toughness and dimensional stability of PC, and the lubricity and good chemical and heat resistance of crystalline PBT. Typical Applications of PC+PBT material Gear cases Automotive bumpers Applications which require – chemical and corrosion resistance – high heat resistance – high impact strength over wide temperature ranges – high dimensional stability Plastic PC+PBT Injection Molding Processing Conditions
Read more →Polycarbonate-acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene blend (PC+ABS) combines the properties of PC and ABS, that is, the high processibility of ABS with the excellent mechanical properties and the impact and heat resistance of PC. The ratio of the two components affects the heat resistance. The blend exhibits excellent flow characteristics. Typical Applications of Plastic PC+ABS Computer housings Business machine housings Electrical applications Cellular phones Lawn and garden equipment Automotive – instrument panels – interior trim – wheel covers Plastic PC+ABS Injection Molding Processing Conditions
Read more →Polycarbonate (PC) is an amorphous engineering material with exceptionally good impact strength, heat resistance, clarity, stabilizability, flame retardancy, and stain resistance. Typical Applications of Polycarbonate (PC) electronic and business equipment - computer parts - connectors appliances - food processors - refrigerator drawers automotive - head lights - tail lights - instrument panels Plastic PC Injection Molding Processing Conditions Chemical and Physical Properties of Polycarbonate (PC) PC is a polyester of carbonic acid. All general-purpose polycarbonates are based on bisphenol A. The bisphenol A component of the molecule contributes to the high glass transition temperature (150°C [302°F]). The rotational mobility of the carbonyl group within the molecule contributes to the high ductility and toughness of the material. The notched Izod impact strength of PC is very high and mold shrinkage is low and consistent [0.1–0.2 mm/mm]. High molecular weight PCs (which translate to low MFR) have higher mechanical properties, but processibility of such grades becomes difficult. The type of PC chosen for an application should be based on the desired criteria. For high-impact properties, use a low-MFR PC; conversely, for optimal
Read more →